Crural fascia - leg fascia. It contains two facets for.
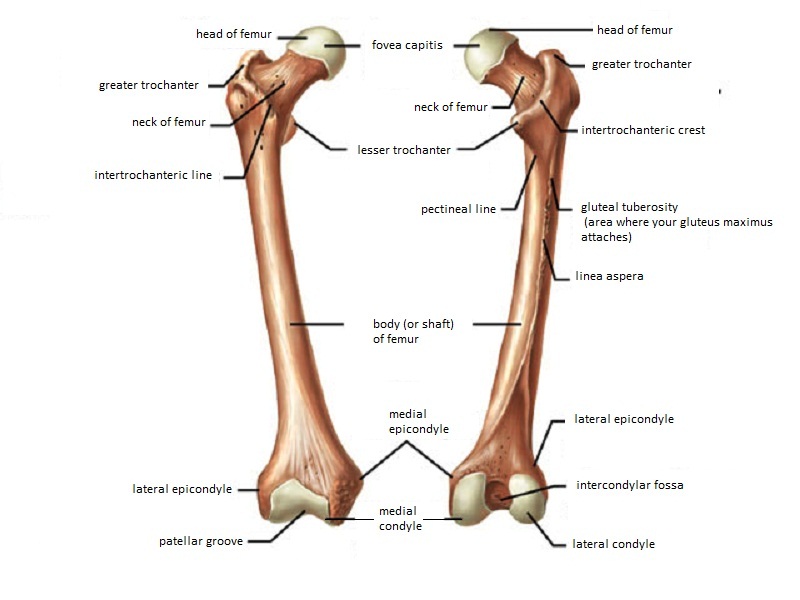
Femur Anatomy And Attachments Bone And Spine
The medial and lateral collateral ligaments of the knee originate from their respective epicondyles.

. N544 TG3-02 Femoral n. Patellar surface of femur. Radial fossa coronoid fossa olecranon fossa.
The lateral epicondyle of the femur smaller and less prominent than the medial epicondyle gives attachment to the fibular collateral ligament of the knee-joint. The Femur has a Greater Lessor Trochanter. It also contains both medial and lateral condyles.
Greater and lesser trochanters of the femur. The purpose of this study was to develop an accurate reliable and easily applicable method for determining the anatomical location of the joint line during revision knee arthroplasty. The thigh bone is called the Femur.
Femur Pelvic Bone Connection. 4 rows The medial and lateral lips unite along the middle third of the femoral shaft traveling. Which bone does not.
Femur - largest long bone Medial lateral epicondyles Tibia Medial malleolus - medial ankle Fibula Lateral malleolus - lateral ankle Investing Fascia Fascia lata - envelopes thigh Iliotibial tract - lateral thickening attached to lat. Intertrochantic line of femur. The medial and lateral condyles are found on the distal end of the femur and those articulate with the knee joint.
They usually form part of a more complex fracture around the femoral component. Medial and lateral epicondyles of the femur d. The medial condyle is larger than the lateral outer condyle due to more weight bearing caused by the centre of mass being medial to the knee.
Medial and lateral condyles of the femur c. Adductor tubercle Patella N507TG3-06TG3-56 N511. The medial and lateral condyles of the tibia articulate with the a.
Lateral femoral cutaneous n. Medial condyle is much larger and bears more weight. The medial and lateral condyle of the tibia are shown in figure 1.
Above and behind the lateral epicondyle is an area for the origin of the lateral head of the gastrocnemius above and to the medial side of which the plantaris arises. The distal end is marked by the presence of the medial and lateral condyles which join with the tibia and patella forming the knee joint. Apex of the patella b.
Directly below it is a small depression from which a smooth well-marked groove curves obliquely upward and backward to the posterior extremity of the condyle. Line at the bottom between the circles. Lateral epicondyles of femur.
Intercondylar fossa a deep notch on the posterior surface of the femur between the two condyles. Medial and lateral epicondyles Bony. These fractures are classified by UCPF as V3-A.
Medial lateral epicondyles Pectineal line of femur. The structure indicated is the lateral femoral condyleThe distal end of the femur forms two rounded condyles which articulate with the tibia below and the patella anteriorly the medial condyle and the lateral condyleThe linea aspera is a roughened crest of bone on the posterior aspect of the femur. Medial condyle of femur.
Medial and lateral condyles Rounded areas at the end of the femur. Medial and lateral supracondylar ridges. The medial and lateral condyles form the proximal part of the body of femur and articulate with the proximal part of tibia to form the femorotibial joint.
The human femur can resist forces of 1800 to 2500 pounds so it. Directly below it is a small depression from which a smooth well-marked groove curves obliquely upward and backward to the posterior extr. Bones and area to remember.
Head of the fibula e. Intercondylar fossa of femur. The structure indicated is the medial epicondyle of the humerus.
Medial and lateral epicondyles. Tibia refers to the shin bone. Isolated medial or lateral epicondyle fractures are rare.
Directly below it is a small depression from which a smooth well-marked groove curves obliquely upward and backward to the posterior extremity of the condyle. Lateral Medial Epicondyles. The transepicondylar width TEW the perpendicular distance between the medial and lateral epicondyles and the distal articular surfaces DMAD DLAD and the distance between.
Medial and lateral epicondyles bony elevations on the non-articular areas of the condyles. On the femur two types of condyles occur in the knee joint. The posterior and inferior surfaces connect with the tibia and menisci of the knee while the anterior surface connects with the patella.
The medial condyle is one of the two projections on the lower extremity of femur the other being the lateral condyle. N500 TG3-17 N540 TG3-63 Anterior femoral cutaneous nn. Medial and lateral condyle.
Tibial condyle Saphenous opening - for greater saphenous v. The distal end of the humerus consists of several features. The lateral epicondyle of the femur smaller and less prominent than the medial epicondyle gives attachment to the fibular collateral ligament of the knee-joint.
The epicondyles and trochanters are all important attachment sites for various muscles. Condyle consisting of the capitulum and trochlea. Medial epicondyles of femur.
There are two condyles found on the proximal end of the tibia and those are known as the medial and lateral condyles of tibia. Distally the linea aspera forms two ridges known as. Know the Head of the Femur and that it attaches to the hip joint called the Acetabulum.
They are separated by the deep intercondylar fossa proximally bounded by the horizontal intercondylar line. The articular surface of the lower end of the femur occupies the anterior inferior and posterior surfaces of the condyles. Lateral condyle is broader than medial condyle of the femur.
When the femur is in its natural oblique position however the lower surfaces of the two condyles lie. The lateral epicondyle of the femur smaller and less prominent than the medial epicondyle gives attachment to the fibular collateral ligament of the knee-joint. The medial epicondyle is the larger.
The lateral condyle is the more prominent and is the broader both in its antero-posterior and transverse diameters. The medial condyle is the longer and when the femur is held with its body perpendicular projects to a lower level. Lateral condyle of femur.
Orif Lag Screw For Lateral Medial Femoral Epicondyle Fracture

Lateral Epicondyle Of The Femur Wikipedia

Femur An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
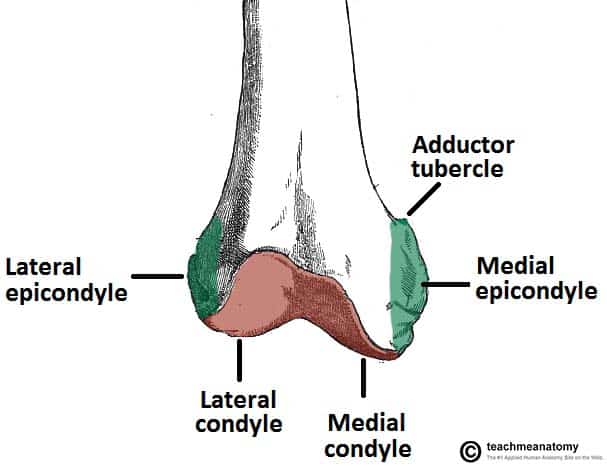
The Femur Proximal Distal Shaft Teachmeanatomy

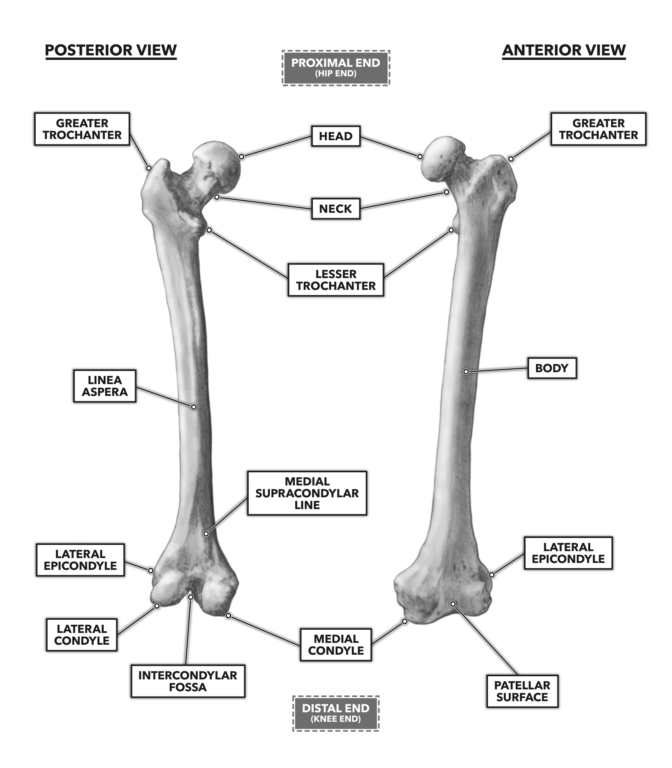
0 comments
Post a Comment